Factors that Affect Body Temperature
No one temperature is normal for all people. Many factors affect body temperature, including:
- Age
- Normally an adult’s body temperature ranges between 96.8 to 100.4 degrees Fahrenheit. (That’s 36 to 38 degrees on the Centigrade scale)
- Older adults have a narrow range of body temperature, averaging around 96.8 degrees Fahrenheit (36 degrees Centigrade). Low body temperatures, 95 degrees Fahrenheit (35 degrees Centigrade) are normal for older adults in cold weather.
- Exercise – Exercise increases body temperature by increasing our metabolism. A long distance runner might have a body temperature as high as 105.8 degrees Fahrenheit (41 degrees Centigrade) after just finishing a long run.
- Hormones – Women usually have greater changes in body temperature than men.
- Menstruation – When a woman has her monthly period (menstruates), body temperatures go up and down. The hormone progesterone affects this cycle. When progesterone levels are low, body temperature is lower than normal. This continues until ovulation.
- During ovulation, progesterone levels rise, thus the body temperature rises. When the body temperature goes up, a woman is more fertile, a time to try to become pregnant. Taking a temperature to check for ovulation requires a special thermometer that measures temperature to 1/100th of a degree.
- Menopause – During menopause women often have hot flashes, lasting from 30 seconds to up to 5 minutes. The temperature of a woman’s skin will rise quickly and there will be sweating.
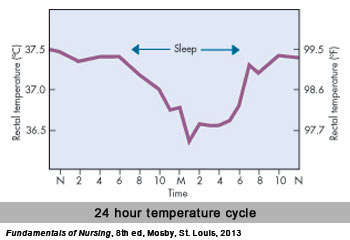
- Daily Cycle – During a normal 24 hour day, the body temperature goes up and down (See Graph). Normally the body temperature is lowest between 1:00 and 4:00 am. The temperature rises during the day, to reach its highest point at about 6:00 pm.
- Stress – Physical and emotional stress increase body temperature. A person who is anxious will likely have an increase in temperature.
- Environment – The outside temperature affects body temperature. Exposure to extreme heat, such as working out in the hot sun, will increase the body temperature. Similarly, if you are out in the cold weather, without proper clothing, the body temperature will fall.
Fever
A fever is an abnormally high body temperature. It is the body’s way to fight infection.
- In adults, a temperature taken by mouth that is above 100.5 degrees Fahrenheit (38 degrees Centigrade) or higher is a fever.
- In adults a rectal or ear temperature above 101.5 degrees Fahrenheit (38.6 degrees Centigrade) or higher is a fever.
Most doctors will not treat an adult’s fever until it is over 102.2 degrees Fahrenheit (39° Centigrade). However, call the doctor for any fever that lasts longer than 48 to 72 hours, especially in older adults.
Causes of Fever
Causes of fever include:
- Infection, the most common cause of a fever.
- Severe injury or trauma to the body, such as a heart attack, stroke, or burn.
- Over exposure to the heat resulting in heat stroke or heat exhaustion.
- Cancer – certain cancers such as leukemia , Hodgkin’s lymphoma, and lung cancer result in fever.
- Other medical conditions such as arthritis and hyperthyroidism
- Drugs – drug fever is becoming more commonly recognized when a person starts a new medicine. The risk for developing drug fever increases with the number of drugs a person takes, especially in the elderly. Drugs known to cause fever include:
- Antibiotics (fights infection)
- Anticholinergics (medicines that treat parkinson’s disease)
- Antihistamines (most allergy medicines)
- Amphetamines ( stimulant drugs)
- Anti-convulsants (treat seizures)
- Anti-tubuculosis(TB) drugs
- Barbituates (drugs that make you relaxed or sleepy)
- Interferon (drugs given to improve immune function)
Signs of Fever
- Skin feels warm and dry to touch
- Skin is flushed
- Lack of energy
- Restlessness
- Developing confusion
- Lack of interest in eating
- Remember in the very old, an increase in temperature may not be the first sign of infection.
- Chills may occur when people have a temperature, indicating a serious infection.
Ways to Measure Temperature
This table explains the different ways to measure body temperature and the pros and cons of each.
|
Route |
Pros |
Cons |
|
Oral (Mouth)  |
Easy to insert and accurate |
Do not use if person had mouth surgery, has a history of seizures, or has nasal stuffiness or shaking chills. |
|
Rectum  |
Very accurate, Best choice for infants |
Use when you cannot get an oral temperature because the person cannot safely and correctly hold a thermometer in their mouth. |
|
Arm Pit (axilla) |
Safe and easy to insert. |
Less accurate than oral or rectal. May be more accurate than oral for persons who breathe with their mouth open or cannot close their mouth tightly around a thermometer. |
|
Skin |
Safe to use |
Do not use if person is sweating. |
|
Ear  |
Accurate, rapid measurement |
Earwax distorts the reading. |
|
Temporal |
More accurate than the ear thermometer in infants, and it is better tolerated by infants that the rectal. |
Not as accurate as the rectal temperature. Should only be used for screening. Thermometer is used infrequently in hospitals. |
|
Types of thermometers
 Digital thermometer – use for the mouth, rectum and the armpit. The thermometer is plastic with a narrow temperature probe at one end and a display window at the other. It contains a computer chip. Place the narrow probe in the mouth, rectum or armpit. The thermometer will show a reading in seconds often with an alarm when the reading is complete.
Digital thermometer – use for the mouth, rectum and the armpit. The thermometer is plastic with a narrow temperature probe at one end and a display window at the other. It contains a computer chip. Place the narrow probe in the mouth, rectum or armpit. The thermometer will show a reading in seconds often with an alarm when the reading is complete. Disposable thermometer – use for the mouth and the armpit. Thermometer is a disposable thin strip of plastic with a temperature sensor on one end. The dots change colors at different temperatures. You can take an oral reading in about 60 seconds. A temperature in the armpit will take about 3 minutes. Some can be reused, but most are single use .
Disposable thermometer – use for the mouth and the armpit. Thermometer is a disposable thin strip of plastic with a temperature sensor on one end. The dots change colors at different temperatures. You can take an oral reading in about 60 seconds. A temperature in the armpit will take about 3 minutes. Some can be reused, but most are single use .- Ear thermometer – use for the ear. An infrared sensor detects heat from the ear drum. Place the cone shaped sensor in the ear. The thermometer registers a temperature in 2 to 3 seconds after you place it in the ear canal.
 Skin thermometer – use on the skin. Press the soft disc against the forehead. It digitally displays the temperature. Other skin thermometers have thin pieces of plastic with numbers on them. Place the strip against the person’s forehead and the temperature makes numbers change colors or light up.
Skin thermometer – use on the skin. Press the soft disc against the forehead. It digitally displays the temperature. Other skin thermometers have thin pieces of plastic with numbers on them. Place the strip against the person’s forehead and the temperature makes numbers change colors or light up. - Temporal Artery Thermometer – Has not been shown to be as accurate as the rectal thermometer in children. Not commonly used in adults.
Skin thermometers are not as accurate as digital or ear thermometers but may be used to determine if a temperature is present. If you get a high reading, recheck the temperature with one of the other thermometers listed above.
Fahrenheit versus Centigrade
A thermometer has either a Fahrenheit or Centigrade (Celsius) scale. Use the same scale consistently so that you can easily detect an abnormal temperature.
Heat Related Illness
A person develops a heat related illness when the body’s ability to control temperature becomes overloaded. The body suddenly cannot cool itself by sweating. This occurs most often when a person works or exercises in very hot weather. The body temperature rises rapidly. A hot, humid climate poses the greatest risk.
Adults most at risk for fever
- Adults over age 65
- People overweight
- People who are chronically ill (Heart disease, high blood pressure)
Heat Stroke
The most serious heat-related illness. It causes severe dehydration, which can be fatal if not treated. Emergency treatment is needed. Body temperature rises to above 103 degrees Fahrenheit (39.4 Centigrade) or higher in 10 to 15 minutes. In addition the person will have:
- Red, hot and dry skin with no sweating
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- Confusion
- Agitation
- Throbbing headache
- Rapid, strong pulse
- Difficulty breathing
- Seizures
- Loss of consciousness
Heat Exhaustion
This is a milder form of heat-related illness. It usually develops after being in very high temperatures for several days and not drinking enough fluids. Heat exhaustion is most common in people who work in hot environments.
A person with heat exhaustion has: